Hamburg, 14 March 2024 - Have you had the opportunity to explore the Bitcoin Whitepaper? It’s an eight-page masterpiece that represents a paradigm shift in financial infrastructure. In this article, we will delve into some key insights from it.
Bitcoin Network
The Bitcoin network operates as a decentralized peer-to-peer electronic payment system founded on cryptographic proof rather than reliance on trust. Transactions are transparent to the public, showcasing the movement of funds between parties while preserving anonymity. Unlike traditional networks, Bitcoin nodes operate without the need for identification, and messages are not constrained to specific routes, relying instead on best-effort delivery. Nodes possess the flexibility to join or depart the network at will, seamlessly integrating back into the system upon their return, supported by the acceptance of the Proof of Work (PoW) chain as evidence of past transactions. In the Bitcoin ecosystem, nodes wield influence through their computational power, participating in the network’s decision-making processes.
The Bitcoin network facilitates online payments directly between parties, by passing the need for intermediaries like traditional financial institutions. Unlike the traditional system, where bank mediation escalates transaction costs, Bitcoin operates differently. While it’s true that criminals can potentially leverage Bitcoin for illicit activities, the network itself is designed to minimize fraud.
One of the network’s primary innovations lies in addressing the double-spending issue without relying on a trusted third party. Introducing such an intermediary would undermine Bitcoin’s core advantages. Instead, the peer-to-peer (P2P) nature of the Bitcoin network emerged as a solution to this crucial challenge.
Transactions on Bitcoin Network
In the Bitcoin network, an electronic coin is conceptualized as a chain of digital signatures, forming a decentralized ledger. The longest chain in this network serves as irrefutable proof of the sequence of events witnessed, derived from the largest accumulation of CPU power. Transactions need not reach every node in the network; widespread dissemination ensures their eventual inclusion in a block. Moreover, the broadcast mechanism for blocks exhibits resilience to dropped messages; nodes autonomously request missed blocks upon realizing their absence.
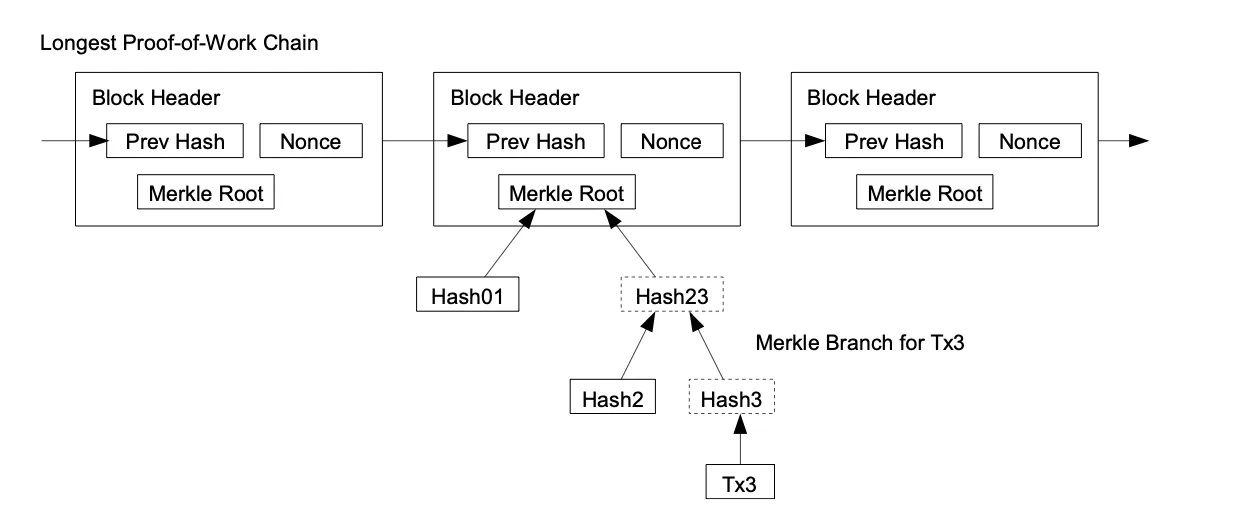
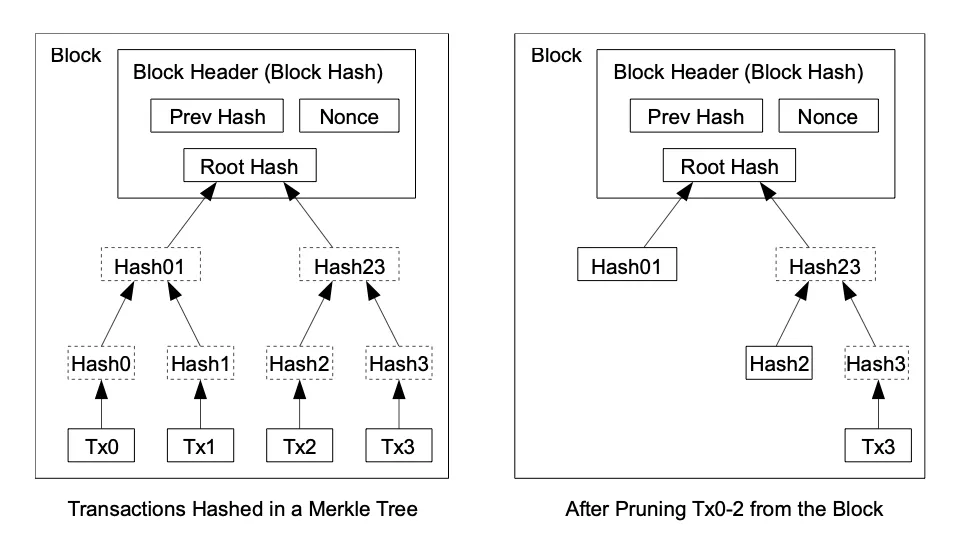
The network’s incentive structure relies on transaction fees. Should a transaction’s output value be less than its input value, the surplus constitutes a transaction fee, augmenting the overall incentive of the block containing the transaction. These incentives foster honesty among nodes, as it is economically advantageous to uphold integrity. To conserve disk space while maintaining block integrity, transactions are hashed within a Merkle tree structure.
Nodes in the Bitcoin network signal acceptance of valid blocks and repudiate invalid ones by dedicating computational resources to extend the blockchain with valid blocks while refusing to engage with invalid ones.
How does it work?
The Bitcoin network timestamps transactions through a process of hashing them into an unbroken chain of hash-based Proof of Work, creating an immutable record. Any attempt to alter the record would necessitate redoing the extensive proof-of-work, making it practically infeasible to tamper with.
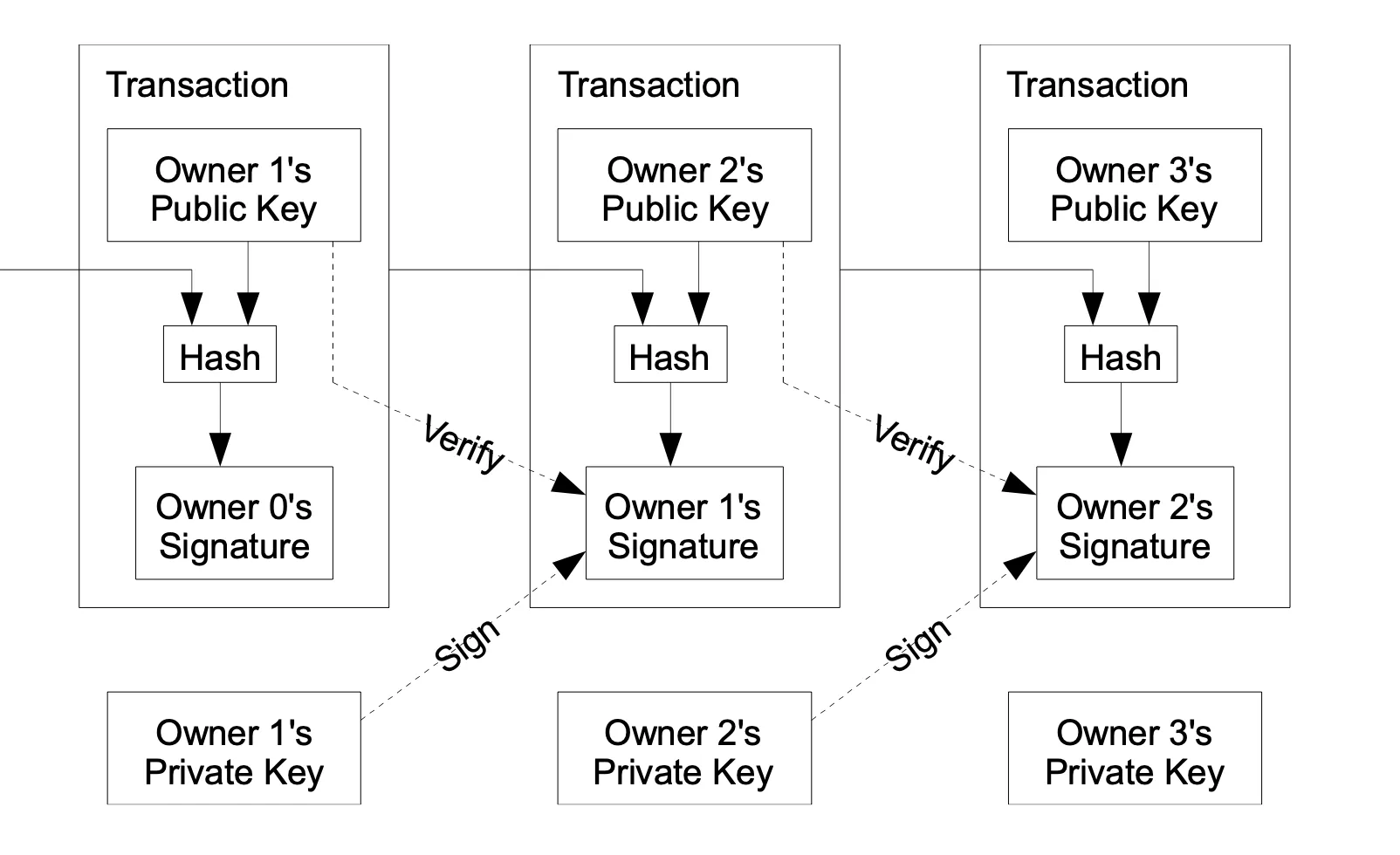
Ownership transfer of coins occurs when the current owner digitally signs a hash of the preceding transaction along with the public key of the next owner, appending this information to the coin. This process enables payees to verify ownership chains by confirming the digital signatures.
Verifying the absence of a transaction requires awareness of all transactions. To validate payments, it’s essential to maintain a copy of the block headers from the longest Proof of Work chain, ensuring integrity and security within the network.
Steps to run the network
- New transactions are promptly broadcasted to every node within the network.
- Each individual node gathers these new transactions and organizes them into a block.
- Every node engages in the task of solving a complex proof-of-work puzzle for its respective block.
- Upon successfully finding a valid proof-of-work solution, the node disseminates the completed block to all other nodes in the network.
- Nodes meticulously scrutinize the incoming block, accepting it only if all contained transactions are deemed valid and have not already been spent.
- Demonstrating consensus, nodes signify their acknowledgment and approval of the block by actively contributing to the creation of the subsequent block in the blockchain, utilizing the hash of the accepted block as the preceding hash reference.
Challenges of Bitcoin network
The integrity of the Bitcoin network is jeopardized when a coalition of nodes wielding the majority of CPU power collaborates to undermine its security. This scenario poses a significant threat to the network’s stability and trustworthiness.
One of Bitcoin’s inherent challenges is the inability of the payee to conclusively verify the absence of double spending by any previous owners of a coin. Traditional remedies to this problem involve the introduction of a centralized authority or mint tasked with scrutinizing each transaction for potential double spending. However, this approach places undue reliance on the integrity of the minting entity, akin to entrusting a bank with every financial transaction.
Should an adversary endeavor to alter a past block, they must undertake the formidable task of redoing the Proof of Work for not only that block but also all subsequent blocks, endeavoring to surpass the collective work of honest nodes. The probability of a slower attacker overtaking the honest chain diminishes exponentially with each subsequent block added.
In cases where two nodes simultaneously broadcast different versions of the next block, network consensus dictates that nodes prioritize the longest chain as the correct one, diligently extending it. However, nodes retain the alternative branch in reserve, awaiting further developments. Resolution occurs organically when the next Proof of Work is discovered, tipping the balance in favor of the lengthier chain.
To fortify the network against attackers, nodes heed alerts from their peers detecting invalid blocks. User software promptly downloads these full blocks and flagged transactions to verify inconsistencies, effectively thwarting potential threats. Despite these safeguards, it remains conceivable for a malicious actor within the Bitcoin network to construct an alternate chain at a pace exceeding that of the honest chain.
coinIX and Bitcoin
The recovery of the Bitcoin price and the approval of Bitcoin ETFs greatly help to alleviate the reservations that still exist in the financial sector regarding crypto and blockchain. Anyone arguing that Bitcoin has no intrinsic value, needs to recognize that the value of an object is determined by supply and demand, not by its properties. The possibility embodied by Bitcoin that units of value can be transferred quickly, securely, and transparently from one wallet to another without the need for an intermediary or even a human has tremendous potential. Bitcoin is also a part of the coinIX portfolio. Hence, our portfolio’s value thrives on the positive bitcoin news.
Conclusion
The Bitcoin Whitepaper remains a seminal document that laid the foundation for the revolutionary cryptocurrency ecosystem we know today. Satoshi Nakamoto’s ingenious solution to the double-spending problem through decentralized consensus and Proof of Work has ushered in a new era of financial autonomy and transparency.
As we continue to witness the evolution of blockchain technology and its applications, it’s crucial to reflect on the principles outlined in the Bitcoin Whitepaper, which continue to shape the future of finance and decentralization.
About coinIX
coinIX GmbH & Co KGaA, based in Hamburg, is a listed In company and has been investing in the broad spectrum of blockchain innovation since 2017. This includes the next level of digitalization in traditional industries, as well as new fields such as Decentralized Finance (DeFi). For this purpose, coinIX invests in equity of startups, early token projects and liquid cryptocurrencies. It offers a listed share that is traded on the open market of the Düsseldorf Stock Exchange.
(WKN: A2LQ1G | ISIN: DE000A2LQ1G5 | Ticker: XCX)

 en
en