Hamburg, 7 March 2024 - If you’ve always considered Bitcoin to be solely a digital payment method with limited use cases, it’s time to reconsider. While Ethereum has traditionally been associated with non-fungible tokens (NFTs), the landscape is evolving, with Bitcoin now entering the NFT arena. What’s intriguing is that unlike Ethereum or Solana, where NFTs rely on off-chain metadata, Bitcoin NFTs can actually store digital assets directly on-chain within transaction witness data. Let us delve deeper:
You’re likely familiar with satoshis, the smallest unit of Bitcoin. With 100,000,000 satoshis in a single Bitcoin, they form the basis of Bitcoin ordinals, a system designed to imbue satoshis with non-fungible properties necessary for NFT creation. Bitcoin ordinals protocol facilitates the attachment of images, videos, and texts to individual satoshis, allowing for the direct creation of NFTs on the Bitcoin blockchain. These NFTs, referred to as ordinal NFTs, represent a novel frontier within the Bitcoin network.
Beyond their role in financial transactions, Bitcoin ordinals open up a realm of possibilities. They allow for the attachment of ordinal satoshis to individual security tokens or stablecoins, paving the way for enhanced utility within the blockchain ecosystem. Moreover, they facilitate the execution of smart contracts on the Bitcoin network, expanding its functionality without necessitating changes to the underlying protocol. Notably, the genesis of Bitcoin ordinals traces back to the first satoshi ever minted in 2008.
However, amidst the excitement, there are some criticisms surrounding Bitcoin ordinals. Some argue that they utilize block space inefficiently, potentially leading to increased Bitcoin transaction fees and slower transaction times in the future.
Bitcoin Updates
Bitcoin NFTs have been around for a while, but it took two significant updates to Bitcoin to truly make them a reality: SegWit and Taproot. SegWit, or segregated witness, was introduced in 2017 as a Bitcoin update, resulting in a soft fork of the blockchain. Witness data, which comprises the sender’s digital signature in a transaction, is crucial to the Bitcoin protocol. With SegWit, witness information is separated from transaction data and stored in a distinct data structure on the blockchain. This separation effectively increases Bitcoin’s block size, as transactions no longer need to include witness data. This enhancement paved the path for users to embed image and video data directly into the witness script, alongside digital signatures and other validation information.
Originally, witness data was devised to overcome the stringent limitations of the block size limit, enabling optional, arbitrary data transmission, and preventing unintentional transaction malleability.
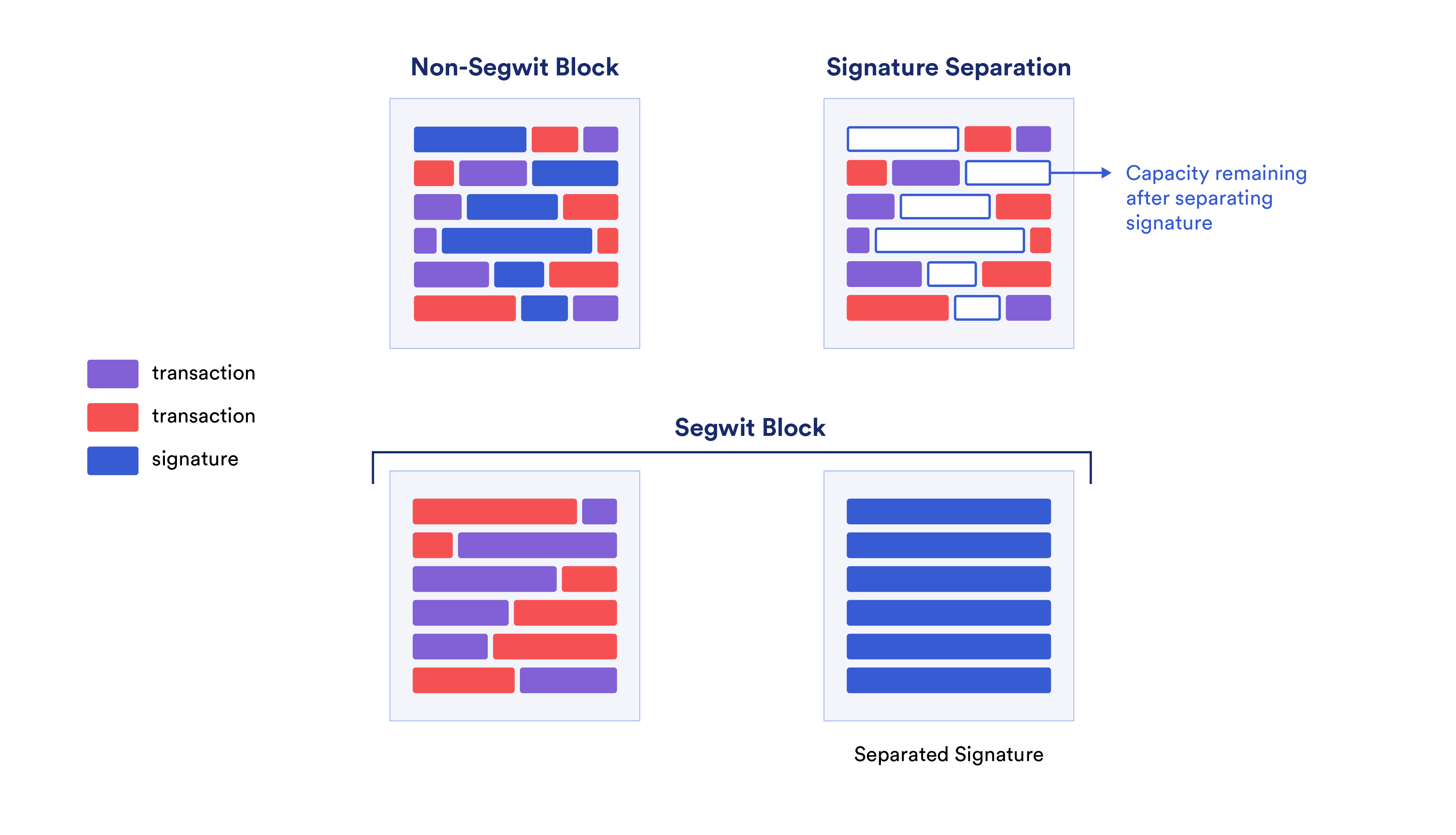
Source: Chainlink
Taproot, a significant Bitcoin update introduced in 2021, brought forth a new era with its novel Bitcoin address format, pivotal for the Bitcoin ordinals protocol in identifying specific satoshis. Beyond its address format innovation, Taproot sets goals in enhancing privacy, security, and scalability within the Bitcoin network while ushering in a new wave of sophistication for Bitcoin-based smart contracts (time-locked contracts). Taproot-Compatible wallets are Metamask, Binance Wallet, Coinhub, Frontier Wallet, Uniswap Wallet, Zerion Wallet, etc.
How to create Ordinal NFTs
Bitcoin ordinals can be effortlessly generated through user-friendly no-code ordinal minting applications or streamlined command-line interfaces. In the realm of no-code applications, users simply transmit an ordinal SAT to Taproot-compatible wallets, seamlessly incorporating data and metadata as integral components of the transaction. Upon completion, the minting process ensues, with the inscription seamlessly etched onto the first satoshi of the transaction’s initial output.
Evolution of Bitcoin NFTs
2012:
- colored coins laid the foundation for Bitcoin NFTs, revolutionizing fungible cryptocurrencies by unlocking new possibilities such as representing shares and maintaining ownership records.
2014:
- Quantum, a piece of digital art crafted by Jennifer and Kevin McCo, marked a significant milestone in the NFT space. In 2014, Kevin transformed this artwork into an NFT, laying the groundwork for what would become the very first NFT ever created.
- Counterparty, a metaprotocol designed to enhance the capabilities of the Bitcoin blockchain. Acting as a layer 2 blockchain technology provider, Counterparty facilitates asset issuance and smart contracts, thus enabling the creation of Bitcoin-based NFTs.
- Omni, stands as a versatile platform dedicated to crafting and trading custom digital assets and currencies. By serving as a software layer atop Bitcoin,Omni empowers users to leverage next-generation features within the Bitcoin blockchain ecosystem.
- OP_return is a function integral to Bitcoin transactions. OP_return allows for the inclusion of third-party information, such as metadata or inscriptions, without the transfer of funds. Initially limited to 80 bytes,
2015:
- Spells of Genesis holds the distinction of being the first-ever blockchain-based mobile game. It seamlessly blends the strategic elements of Trading Card Games (TCG) with the fast-paced excitement of arcade-style gameplay. Since 2015, their collection of cards, minted directly onto the blockchain, has been a landmark moment in the history of NFTs.
2016:
- The Rare Pepe NFTs collection comprises 36 series, each featuring 50 unique Pepe images with different levels of rarity and availability. These iconic digital assets made their debut in September 2016, being mined in block number 428,919 on the Bitcoin blockchain before being released on the Counterparty platform.
2017:
- SegWit brought a significant change to the Bitcoin network. Instead of the traditional 1MB block limit, SegWit introduced a 4MB block limit, which translates to 4,000,000 weight units. This adjustment meant that while blocks with only legacy transactions were still restricted to 1MB, blocks containing SegWit transactions could now accommodate up to 4MB of data.
2021
- Taproot was introduced. Bitcoin transactions gained newfound flexibility. This update allowed for the inclusion of additional data within transactions, empowering users to create inscriptions alongside their transactions.
2022:
- Bitcoin Ordinals were Introduced by Casey Rodarmor. It was conceptualized on the foundation of ordinal theory, which employs an arbitrary yet logical ordering system that assigns a unique number to each Satoshi, based on the order in which they are mined.
2023
- Luxor Pool minted the 1st 4MB inscription.
- The 1st ordinal wallets were created.
2024
- Bitcoin ordinals are gaining attention and new market places are emerging
Conclusion
Bitcoin ordinals represent innovative advancements in the Blockchain industry. Embracing these developments with cautious optimism can lead to a deeper understanding of the potential they hold for shaping the future of finance, art, and digital ownership.
coinIX and Bitcoin
The recovery of the Bitcoin price and the approval of Bitcoin ETFs greatly help to alleviate the reservations that still exist in the financial sector regarding crypto and blockchain. Anyone arguing that Bitcoin has no intrinsic value, needs to recognize that the value of an object is determined by supply and demand, not by its properties. The possibility embodied by Bitcoin that units of value can be transferred quickly, securely, and transparently from one wallet to another without the need for an intermediary or even a human has tremendous potential. Bitcoin is also a part of the coinIX portfolio. Hence, our portfolio’s value thrives on the positive bitcoin news.
About coinIX
coinIX GmbH & Co KGaA, based in Hamburg, is a listed In company and has been investing in the broad spectrum of blockchain innovation since 2017. This includes the next level of digitalization in traditional industries, as well as new fields such as Decentralized Finance (DeFi). For this purpose, coinIX invests in equity of startups, early token projects and liquid cryptocurrencies. It offers a listed share that is traded on the open market of the Düsseldorf Stock Exchange.
(WKN: A2LQ1G | ISIN: DE000A2LQ1G5 | Ticker: XCX)

 en
en